
Chikungunya
Historical Data
-
There are no known cases in Virginia, and had some reported cases from travellers. There is a concern it may spread from travellers who go to places where the disease is common: South America and the Caribbean. There have only been 11 local transmissions in the U.S. from travellers, all in Florida.
-
It is common in Africa, Asia, and some countries in Europe.
Transmission
-
Infected by the bite of a mosquito caused by the virus CHIK.
-
It is transmitted by the Aedes aegypti, Aedes albopictus, and Asian Tiger mosquito.
-
Between mosquitoes biting infected humans and passing it to other humans. Humans are a dead- end host. It could be transmitted by infected blood or mother to child.
Symptoms
-
Fever
-
Joint pain/swelling in multiple joints
-
Body aches
-
Headache
-
Nausea
-
Back pain
-
Rash
-
The illness only lasts about 10 days, but the joint pain may last longer. The relapse of joint pain may last for a few years, but death is uncommon from this illness.
-
There is no treatment.
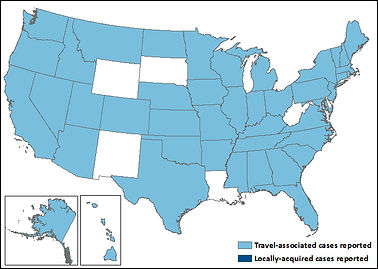
States reporting chikungunya virus disease cases – United States, 2015 (as of January 12, 2016), CDC
Pathogens
-
There is more to be learned about the CHIK virus, but it behaves similarly to the dengue virus. Chikungunya virus is an alpha virus that belongs to the Togaviridae family. It is a single-stranded RNA virus and is approximately 11.8 kb long with a capsid and a phospholipid envelope, like Eastern Equine Encephalitis. An alphavirus is one that is spread by mosquitoes. It is also an arbovirus, which means it occurs in arthropods.


